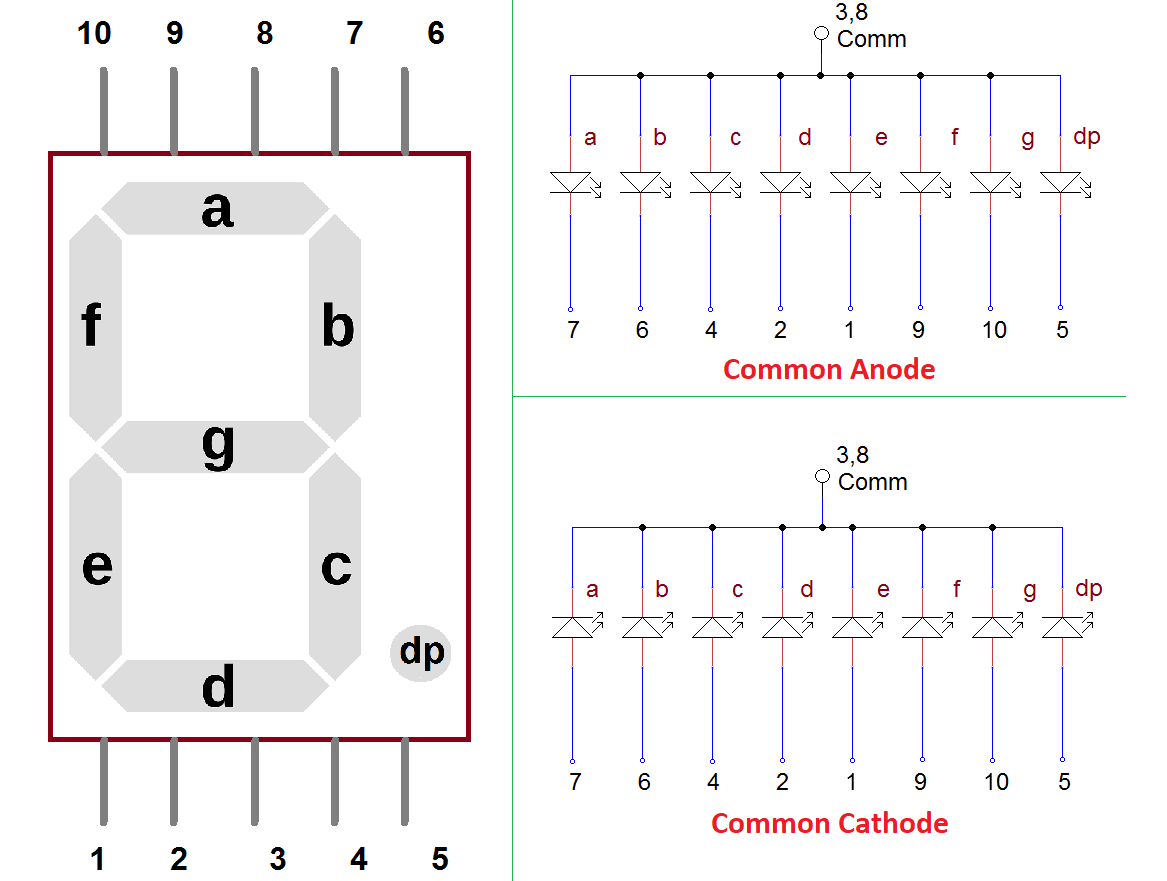
Seven Segment display
NodeMCU
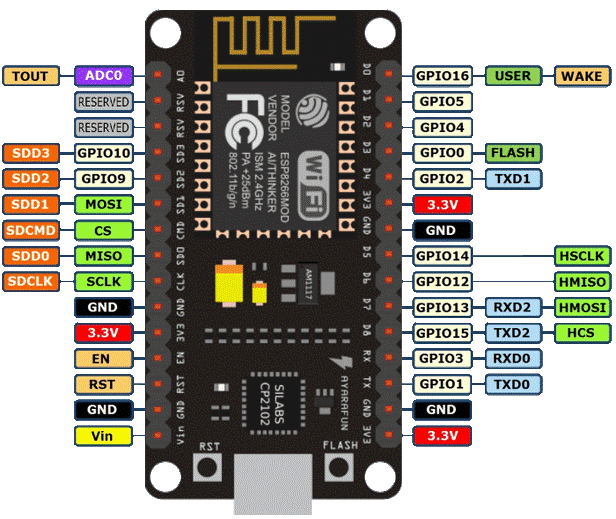
Pin Configuration
Seven segment and NodeMCU pin connections
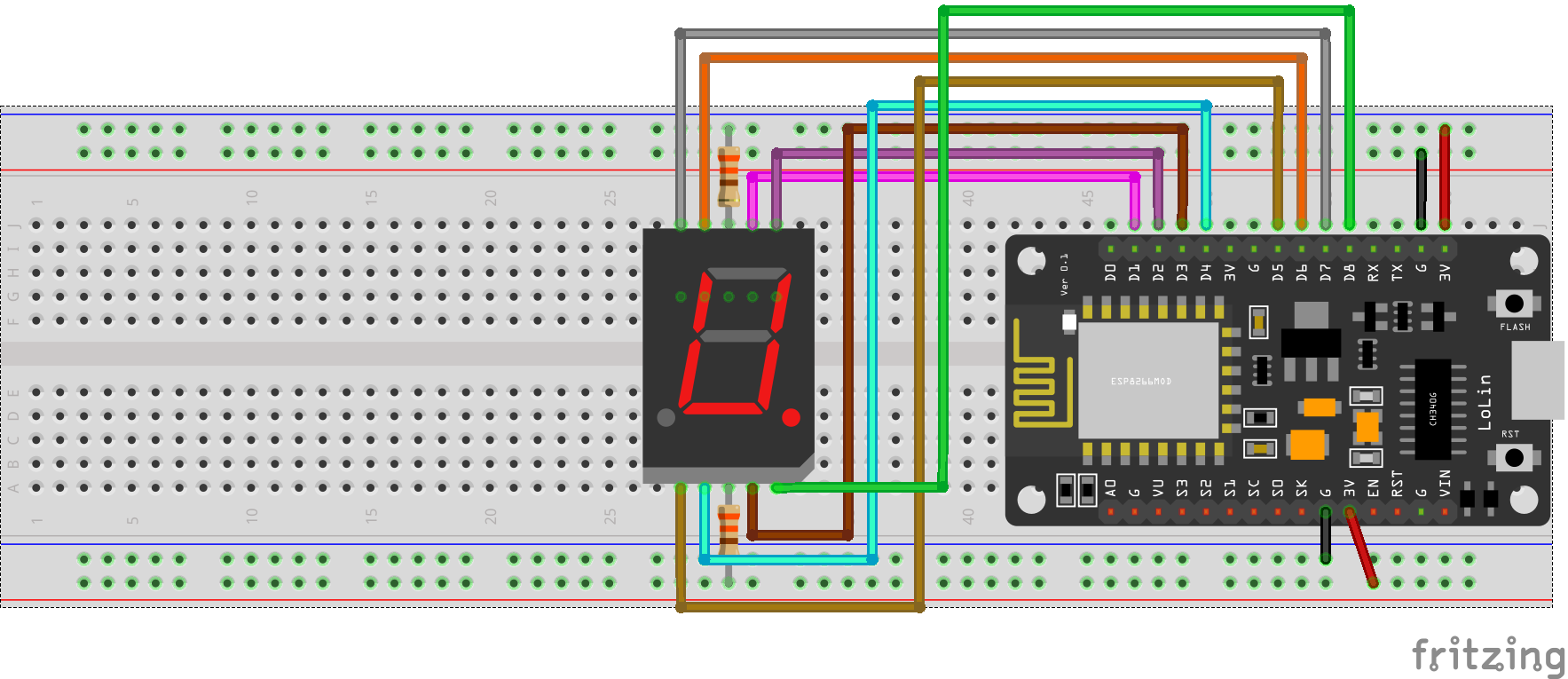
const int A = D1;
const int B = D2;
const int C = D3;
const int D = D4;
const int E = D5;
const int F = D6;
const int G = D7;
const int DP = D8;
void setup() {
pinMode(A, OUTPUT);
pinMode(B, OUTPUT);
pinMode(C, OUTPUT);
pinMode(D, OUTPUT);
pinMode(E, OUTPUT);
pinMode(F, OUTPUT);
pinMode(G, OUTPUT);
pinMode(DP, OUTPUT);
}
void loop() {
ZERO();
delay(1000);
ONE();
delay(1000);
THREE();
delay(1000);
FOUR();
delay(1000);
FIVE();
delay(1000);
SIX();
delay(1000);
SEVEN();
delay(1000);
EIGHT();
delay(1000);
NINE();
delay(1000);
}
void ZERO(){
digitalWrite(A, LOW);
digitalWrite(B, LOW);
digitalWrite(C, LOW);
digitalWrite(D, LOW);
digitalWrite(E, LOW);
digitalWrite(F, LOW);
digitalWrite(G, HIGH);
digitalWrite(DP, HIGH);
}
void ONE(){
digitalWrite(A, HIGH);
digitalWrite(B, LOW);
digitalWrite(C, LOW);
digitalWrite(D, HIGH);
digitalWrite(E, HIGH);
digitalWrite(F, HIGH);
digitalWrite(G, HIGH);
digitalWrite(DP, HIGH);
}
void TWO(){
digitalWrite(A, LOW);
digitalWrite(B, LOW);
digitalWrite(C, HIGH);
digitalWrite(D, LOW);
digitalWrite(E, LOW);
digitalWrite(F, HIGH);
digitalWrite(G, LOW);
digitalWrite(DP, HIGH);
}
void THREE(){
digitalWrite(A, LOW);
digitalWrite(B, LOW);
digitalWrite(C, LOW);
digitalWrite(D, LOW);
digitalWrite(E, HIGH);
digitalWrite(F, HIGH);
digitalWrite(G, LOW);
digitalWrite(DP, HIGH);
}
void FOUR(){
digitalWrite(A, HIGH);
digitalWrite(B, LOW);
digitalWrite(C, LOW);
digitalWrite(D, LOW);
digitalWrite(E, HIGH);
digitalWrite(F, LOW);
digitalWrite(G, LOW);
digitalWrite(DP, HIGH);
}
void FIVE(){
digitalWrite(A, LOW);
digitalWrite(B, HIGH);
digitalWrite(C, LOW);
digitalWrite(D, LOW);
digitalWrite(E, HIGH);
digitalWrite(F, LOW);
digitalWrite(G, LOW);
digitalWrite(DP, HIGH);
}
void SIX(){
digitalWrite(A, LOW);
digitalWrite(B, HIGH);
digitalWrite(C, LOW);
digitalWrite(D, LOW);
digitalWrite(E, LOW);
digitalWrite(F, LOW);
digitalWrite(G, LOW);
digitalWrite(DP, HIGH);
}
void SEVEN(){
digitalWrite(A, LOW);
digitalWrite(B, LOW);
digitalWrite(C, LOW);
digitalWrite(D, HIGH);
digitalWrite(E, HIGH);
digitalWrite(F, HIGH);
digitalWrite(G, HIGH);
digitalWrite(DP, HIGH);
}
void EIGHT(){
digitalWrite(A, LOW);
digitalWrite(B, LOW);
digitalWrite(C, LOW);
digitalWrite(D, LOW);
digitalWrite(E, LOW);
digitalWrite(F, LOW);
digitalWrite(G, LOW);
digitalWrite(DP, HIGH);
}
void NINE(){
digitalWrite(A, LOW);
digitalWrite(B, LOW);
digitalWrite(C, LOW);
digitalWrite(D, LOW);
digitalWrite(E, HIGH);
digitalWrite(F, LOW);
digitalWrite(G, LOW);
digitalWrite(DP, HIGH);
}